Show and Tell, Neural Image Caption Generator: English and Bangla
It ain’t much , but it’s honest work
Hello all! In this blog, I am trying to demonstrate my latest - and hopefully not the last - attempt to generate Captions from images. I tried it before. But this time , (a) I am implementing in PyTorch, (b) implementing the actual paper of 2014 , (c) along with flickr8k dataset , I implemented on - atleast tried to! - Bangla Image Captioninig Dataset! Hope you will enjoy! All codes are available here
Disclaimer


Acknowledgement
To get this work done , i took helps from the computer vision nanodegree repositories of this and this . For English Image captioning , I used Flickr8k Dataset . And for Bengali Image captioning , I took help from the guys this paper, Chittron on Bengali Image Caption generation. Their data is available here
Initializing packages
import os
import cv2
import random
import numpy as np
import random
SEED=1234
np.random.seed(SEED)
import torch
from torch.utils import data
import torch.nn as nn
Loading the data
For loading the data , I wrote two classes . Dataset and Vocabulary. This were inspired by the udacity nanodegree repositories, but i changed according to my project
Vocabulary Class
This class defines the vocabulary. This class uses tokenizer to tokenize the captions . I commented out the start word. Why ? Coming out later
import nltk
import pickle
import os.path
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
nltk.download("punkt")
from collections import Counter
class Vocabulary(object):
def __init__(self,
captions,
vocab_file='./vocab.pkl',
start_word="<start>",
end_word="<end>",
unk_word="<unk>",
annotations_file='../cocoapi/annotations/captions_train2014.json',
vocab_from_file=False,
tokenizer=nltk.tokenize.word_tokenize):
"""Initialize the vocabulary.
Args:
vocab_threshold: Minimum word count threshold.
captions: list of captions
vocab_file: File containing the vocabulary.
start_word: Special word denoting sentence start.
end_word: Special word denoting sentence end.
unk_word: Special word denoting unknown words.
annotations_file: Path for train annotation file.
vocab_from_file: If False, create vocab from scratch & override any existing vocab_file
If True, load vocab from from existing vocab_file, if it exists
"""
self.captions=captions
self.vocab_file = vocab_file
self.start_word = start_word
self.end_word = end_word
self.unk_word = unk_word
self.annotations_file = annotations_file
self.vocab_from_file = vocab_from_file
self.tokenizer=tokenizer
self.get_vocab()
def get_vocab(self):
"""Load the vocabulary from file OR build the vocabulary from scratch."""
if os.path.exists(self.vocab_file) & self.vocab_from_file:
with open(self.vocab_file, 'rb') as f:
vocab = pickle.load(f)
self.word2idx = vocab.word2idx
self.idx2word = vocab.idx2word
print('Vocabulary successfully loaded from vocab.pkl file!')
else:
self.build_vocab()
with open(self.vocab_file, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(self, f)
def build_vocab(self):
"""Populate the dictionaries for converting tokens to integers (and vice-versa)."""
self.init_vocab()
# self.add_word(self.start_word) #
self.add_word(self.end_word)
self.add_word(self.unk_word)
self.add_captions()
def init_vocab(self):
"""Initialize the dictionaries for converting tokens to integers (and vice-versa)."""
self.word2idx = {}
self.idx2word = {}
self.idx = 0
def add_word(self, word):
"""Add a token to the vocabulary."""
if not word in self.word2idx:
self.word2idx[word] = self.idx
self.idx2word[self.idx] = word
self.idx += 1
def add_captions(self):
"""Loop over training captions and add all tokens to the vocabulary that meet or exceed the threshold."""
counter = Counter()
for i, caption in enumerate(self.captions):
tokens = self.tokenizer(caption.lower())
counter.update(tokens)
if i % 1000 == 0:
print("[%d/%d] Tokenizing captions..." % (i, len(self.captions)))
words = [word for word, cnt in counter.items() if cnt >= self.vocab_threshold]
for i, word in enumerate(words):
self.add_word(word)
def __call__(self, word):
if not word in self.word2idx:
return self.word2idx[self.unk_word]
return self.word2idx[word]
def __len__(self):
return len(self.word2idx)
Dataset Class
import cv2
import os
import torch
from torch.utils import data
from torchvision import transforms
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
import random
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
class Dataset(data.Dataset):
def __init__(self,images_folder,
data,
transform,
vocab,
imsize=(224,224),
shuffle=True,
tokenizer=word_tokenize
):
"""images_folder: images path
data: list of tuples containing the name of image and respective captions
vocab: vocabulary object
imsize: tuple, image size
shuffle: bool, will we shuffle the data or not
tokenizer: tokenizer object"""
self.image_folder=images_folder
if shuffle:
random.shuffle(data)
self.data=data
self.transform=transform
self.imsize=imsize
self.vocab=vocab
self.tokenizer=tokenizer
def load_data(self,batch_size=32):
images,captions=[None]*batch_size,[None]*batch_size
for i in range(self.__len__()):
image,caption=self.__getitem__(i)
c,h,w=image.size()
images[i%batch_size]=image.view(-1,c,h,w)
captions[i%batch_size]=caption
if i>0 and i%batch_size==0:
yield images,captions
def __getitem__(self,index):
data =self.data[index]
image_name=data[0]
image=cv2.imread(os.path.join(self.image_folder,image_name))
image=cv2.cvtColor(image,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
image=cv2.resize(image,self.imsize)
image=self.transform(Image.fromarray(image))
caption= data[1]
tokens = self.tokenizer(str(caption).lower())
caption = []
caption.extend([self.vocab(token) for token in tokens])
caption.append(self.vocab(self.vocab.end_word))
caption = torch.Tensor(caption).long()
return image,caption
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data)
I saved the above classes in the python scripts vocabulary.py and dataloader.py
loading The classes
from dataloader import Dataset
from vocabulary import Vocabulary
Here comes the difference
The flickr8k dataset and BanglaLekhaImageCaptions datset are structured in a very different way. But I need to generate the data in the same way. The dataset class takes the image names and captions as list of tuples i.e. [(image_name,caption)] . It will give the output as tensors of images and tokenized tensors of captions
Dataset folder
Flickr8k Dataset
dataset_folder="/floyd/input/flickr8k/"
Generating the lists of tuples with image names and captions
tokens=open(dataset_folder+"Flickr8k.token.txt").read().split("\n")
for token in tokens:
if token=='':
tokens.remove(token)
train_images_text_file=dataset_folder+"Flickr_8k.trainImages.txt"
validation_images_text_file=dataset_folder+"Flickr_8k.devImages.txt"
test_images_text_file=dataset_folder+"Flickr_8k.testImages.txt"
train_images_text=open(train_images_text_file,"r").read()
validation_images_text=open(validation_images_text_file,"r").read()
test_images_text=open(test_images_text_file,"r").read()
train_images_names=train_images_text.split("\n")
validation_images_names=validation_images_text.split("\n")
test_images_names=test_images_text.split("\n")
image_folder= dataset_folder+"Flicker8k_Dataset/"
image_names=[]
captions=[]
train_with_captions=[]
val_with_captions=[]
test_with_captions=[]
for token in tokens:
image_name=token.split("\t")[0].split("#")[0]
caption= token.split("\t")[1]
image_names.append(image_name)
captions.append(caption)
if image_name in train_images_names:
train_with_captions.append((image_name,caption))
elif image_name in validation_images_names:
val_with_captions.append((image_name,caption))
elif image_name in test_images_names:
test_with_captions.append((image_name,caption))
vocab=Vocabulary(vocab_threshold=6,captions=captions)
Image preprocessing
Bengali Image Captions Dataset
dataset_folder="/floyd/input/bangla_image_caption/"
caption_json_path=dataset_folder+"captions.json"
filenames_with_captions=json.load(open(caption_json_path))
from bnltk.tokenize import Tokenizers
t = Tokenizers()
tokenizer = t.bn_word_tokenizer
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
train,test=train_test_split(filenames_with_captions,test_size=0.1)
train,valid=train_test_split(filenames_with_captions,test_size=0.1)
image_names=[]
all_captions=[]
train_with_captions=[]
val_with_captions=[]
test_with_captions=[]
image_folder= dataset_folder+"images/"
for filename_caption in train:
image_name = filename_caption["filename"]
captions=filename_caption["caption"]
for caption in captions:
train_with_captions.append((image_name,caption))
all_captions.append(caption)
for filename_caption in valid:
image_name = filename_caption["filename"]
captions=filename_caption["caption"]
for caption in captions:
val_with_captions.append((image_name,caption))
all_captions.append(caption)
for filename_caption in test:
image_name = filename_caption["filename"]
captions=filename_caption["caption"]
for caption in captions:
test_with_captions.append((image_name,caption))
all_captions.append(caption)
vocab=Vocabulary(vocab_threshold=6,captions=all_captions,tokenizer=t.bn_word_tokenizer)
from torchvision import transforms
# Define a transform to pre-process the training images.
transform_train = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(224), # smaller edge of image resized to 256
transforms.RandomCrop(224), # get 224x224 crop from random location
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), # horizontally flip image with probability=0.5
transforms.ToTensor(), # convert the PIL Image to a tensor
# transforms.Normalize((0.485, 0.456, 0.406), # normalize image for pre-trained model
# (0.229, 0.224, 0.225))
])
Dataset objects
dataset= Dataset(image_folder,train_with_captions,transform_train,vocab)
valid_dataset= Dataset(image_folder,val_with_captions,transform_train,vocab)
test_dataset= Dataset(image_folder,test_with_captions,transform_train,vocab)
Model Definition
Here I am following the model form the paper ,
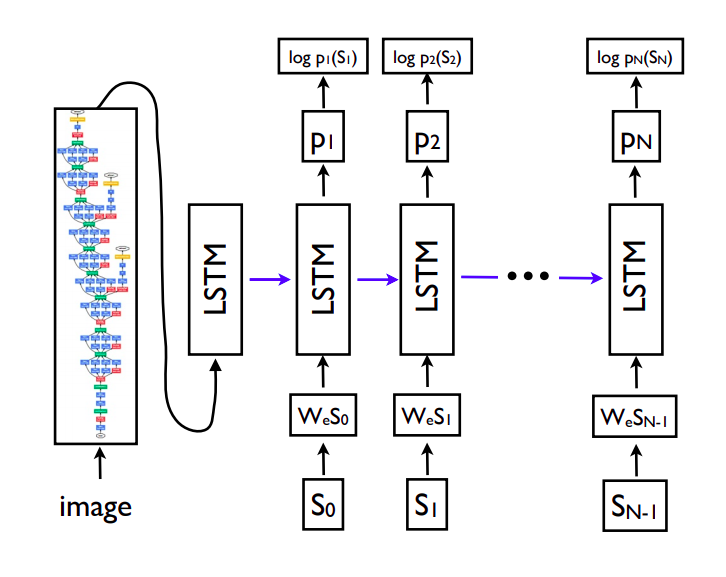
The above image is a screenshot from the paper. Here , s0 is the starting token of the resulting sequence. But I could not get good results from using s0. But when i used the image features itself as the starting token, the result got better. For the CNN encoder, I used VGG16 pretrained model
Encoder
class EncoderVGG(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(EncoderVGG, self).__init__()
model = models.vgg16(pretrained=True)
for param in model.parameters():
param.requires_grad_(False)
normal_modules = list(model.features.children())+list(model.avgpool.children())
classifier_modules=list(model.classifier.children())[:-3]
self.conv_model = nn.Sequential(*normal_modules)
self.classifier_model=nn.Sequential(*classifier_modules)
# self.embed = nn.Linear(resnet.fc.in_features, embed_size)
def forward(self, images):
features = self.conv_model(images)
features = features.view(features.size(0),-1)
features = self.classifier_model(features)
return features
Decoder
This decoder is one layer Lstm network with hidden units of 512. I have used exact same network used in the udacity computer vision nanodegree repository
class DecoderRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, embed_size, hidden_size, vocab_size,batch_size):
''' Initialize the layers of this model.'''
super().__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
# Embedding layer that turns words into a vector of a specified size
self.word_embeddings = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embed_size)
# The LSTM takes embedded word vectors (of a specified size) as input
# and outputs hidden states of size hidden_dim
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=embed_size, \
hidden_size=hidden_size, # LSTM hidden units
num_layers=1, # number of LSTM layer
bias=True, # use bias weights b_ih and b_hh
batch_first=True, # input & output will have batch size as 1st dimension
dropout=0, # Not applying dropout
bidirectional=False, # unidirectional LSTM
)
# The linear layer that maps the hidden state output dimension
# to the number of words we want as output, vocab_size
self.linear = nn.Linear(hidden_size, vocab_size)
self.batch_size=batch_size
# initialize the hidden state
# self.hidden = self.init_hidden()
def init_hidden(self, batch_size):
""" At the start of training, we need to initialize a hidden state;
there will be none because the hidden state is formed based on previously seen data.
So, this function defines a hidden state with all zeroes
The axes semantics are (num_layers, batch_size, hidden_dim)
"""
return (torch.zeros((1, batch_size, self.hidden_size), device=device), \
torch.zeros((1, batch_size, self.hidden_size), device=device))
def forward(self, features, captions):
""" Define the feedforward behavior of the model """
# Discard the <end> word to avoid predicting when <end> is the input of the RNN
# captions = captions[:, :-1]
input_captions=[caption[:-1] for caption in captions]
input_captions=nn.utils.rnn.pad_sequence(input_captions,batch_first=True)
# print(input_captions.size())
input_captions_lengths=[len(input_caption)+1 for input_caption in input_captions]
embeddings = self.word_embeddings(input_captions) # embeddings new shape : (batch_size, captions length - 1, embed_size)
# Initialize the hidden state
batch_size = features.shape[0] # features is of shape (batch_size, embed_size)
self.hidden = self.init_hidden(self.batch_size)
# Create embedded word vectors for each word in the captions
embeddings = torch.cat((features.unsqueeze(1), embeddings), dim=1) # embeddings new shape : (batch_size, caption length, embed_size)
embeddings=nn.utils.rnn.pack_padded_sequence(embeddings,lengths=input_captions_lengths,batch_first=True,enforce_sorted=False)
# Get the output and hidden state by passing the lstm over our word embeddings
# the lstm takes in our embeddings and hidden state
lstm_out, self.hidden = self.lstm(embeddings, self.hidden) # lstm_out shape : (batch_size, caption length, hidden_size)
lstm_out=nn.utils.rnn.pad_packed_sequence(lstm_out,batch_first=True)
#Fully connected layer
outputs = self.linear(lstm_out[0]) # outputs shape : (batch_size, caption length, vocab_size)
return outputs
I have kept the encoder and decoder classes in the script model.py
from model import EncoderVGG
from model import DecoderRNN
from torchvision import models
batch_size = 128 # batch size
vocab_threshold = 6 # minimum word count threshold
vocab_from_file = True # if True, load existing vocab file
embed_size = 4096 # dimensionality of image and word embeddings
hidden_size = 512 # number of features in hidden state of the RNN decoder
num_epochs = 50 # number of training epochs (1 for testing)
save_every = 1 # determines frequency of saving model weights
print_every = 200 # determines window for printing average loss
log_file = 'training_log.txt' # name of file with saved training loss and perplexity
val_log_file = 'validation_log.txt'
vocab_size=len(vocab)
encoder = EncoderVGG()
decoder = DecoderRNN(embed_size, hidden_size, vocab_size,batch_size)
# Move models to GPU if CUDA is available.
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
encoder.to(device)
decoder.to(device)
# Define the loss function.
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().cuda() if torch.cuda.is_available() else nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
Lets look at the first image
image=dataset[0][0]
image=image.data.numpy().transpose((1,2,0))
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.imshow(image)
params = list(decoder.parameters())
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(params, lr=0.001, weight_decay=0.001)
validation_loss_min = np.inf
train_losses=[]
validation_losses=[]
Training!
f = open(log_file, 'w')
validation_f=open(val_log_file,'w')
i_step=0
print_every=100
for epoch in range(1, num_epochs+1):
try:
for images,captions in dataset.load_data(batch_size):
images=torch.cat(images)
# Move batch of images and captions to GPU if CUDA is available.
images_gpu = images.to(device)
captions_gpu = [caption.to(device) for caption in captions]
captions_padded=nn.utils.rnn.pad_sequence(captions_gpu,batch_first=True)
# Zero the gradients.
decoder.zero_grad()
encoder.zero_grad()
# Pass the inputs through the CNN-RNN model.
features = encoder(images_gpu)
outputs = decoder(features, captions_gpu)
# Calculate the batch loss.
# print("outputs.shape: ", outputs.shape)
loss = criterion(outputs.contiguous().view(-1, vocab_size), captions_padded.view(-1))
# Backward pass.
loss.backward()
# Update the parameters in the optimizer.
optimizer.step()
# Get training statistics.
stats = 'Epoch [%d/%d], Step [%d], Loss: %.4f, Perplexity: %5.4f' % (epoch, num_epochs, i_step, loss.item(), np.exp(loss.item()))
# Print training statistics (on same line).
print('\r' + stats, end="")
# Print training statistics to file.
f.write(stats + '\n')
f.flush()
# Print training statistics (on different line).
if i_step % print_every == 0:
print('\r' + stats)
i_step=i_step+1
train_losses.append(loss.item())
except RuntimeError:
print(captions,i_step)
pass
validation_loss=0
validation_iter=1
for images,captions in valid_dataset.load_data(batch_size):
images=torch.cat(images)
# Move batch of images and captions to GPU if CUDA is available.
images = images.to(device)
captions = [caption.to(device) for caption in captions]
captions_padded=nn.utils.rnn.pad_sequence(captions,batch_first=True)
with torch.no_grad():
# Pass the inputs through the CNN-RNN model.
features = encoder(images)
outputs = decoder(features, captions)
# Calculate the batch loss.
# print("outputs.shape: ", outputs.shape)
loss = criterion(outputs.contiguous().view(-1, vocab_size), captions_padded.view(-1))
validation_loss=validation_loss+loss.item()
validation_iter=validation_iter+1
# Get training statistics.
validation_loss = validation_loss/validation_iter
validation_losses.append(validation_loss)
stats = 'Epoch [%d/%d], Step [%d], Validation Loss: %.4f, Perplexity: %5.4f\n' % (epoch, num_epochs, validation_iter, validation_loss, np.exp(validation_loss))
torch.save(decoder.state_dict(), os.path.join('models', 'decoder-%d.pkl' % epoch))
torch.save(encoder.state_dict(), os.path.join('models', 'encoder-%d.pkl' % epoch))
if validation_loss<validation_loss_min:
print("\nmodel improved!")
validation_loss_min=validation_loss
else:
print("\nnot improved yet!")
# Print training statistics (on same line).
print('\n' + stats, end="")
# Print training statistics to file.
validation_f.write(stats + '\n')
validation_f.flush()
# Print training statistics (on different line).
# Close the training log file.
f.close()
validation_f.close()
The models are saved at flickr_models folder. Make sure you have such. The models on Bangla Image captions are saved in bengali_models
encoder.load_state_dict(torch.load("flickr_models/encoder-1.pkl"))#,map_location="cpu"))
decoder.load_state_dict(torch.load("flickr_models/decoder-5.pkl"))#,map_location="cpu"))
encoder.eval()
decoder.eval()
Inference
The following codes are for inference of all the of datasets. The sample function takes features generated from the encoder as input and gives the output. I saved in a seperate folder
target_folder="flickr8k_images_outputs/test/"
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def sample(inputs):
" accepts pre-processed image tensor (inputs) and returns predicted sentence (list of tensor ids of length max_len) "
output = []
batch_size = inputs.shape[0] # batch_size is 1 at inference, inputs shape : (1, 1, embed_size)
hidden = decoder.init_hidden(batch_size) # Get initial hidden state of the LSTM
while True:
lstm_out, hidden = decoder.lstm(inputs, hidden) # lstm_out shape : (1, 1, hidden_size)
outputs = decoder.linear(lstm_out) # outputs shape : (1, 1, vocab_size)
outputs= nn.functional.softmax(outputs,dim=2)
outputs = outputs.squeeze(1) # outputs shape : (1, vocab_size)
_, max_indice = torch.max(outputs, dim=1) # predict the most likely next word, max_indice shape : (1)
output.append(max_indice.cpu().numpy()[0].item()) # storing the word predicted
if (max_indice == 0):
# We predicted the <end> word, so there is no further prediction to do
break
## Prepare to embed the last predicted word to be the new input of the lstm
inputs = decoder.word_embeddings(max_indice) # inputs shape : (1, embed_size)
inputs = inputs.unsqueeze(1) # inputs shape : (1, 1, embed_size)
return output
count=0
for validation_image,validation_caption in test_dataset:
encoder.eval()
decoder.eval()
validation_image=validation_image.to(device)
validation_image=validation_image.view(1,3,224,224)
actual_outputs=validation_caption.cpu().numpy().tolist()
features=encoder(validation_image)
outputs=sample(features.view(1,1,4096))
output_words=[vocab.idx2word[output] for output in outputs]
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(validation_image[0].cpu().numpy().transpose((1,2,0)))
plt.title(" ".join(output_words))
plt.savefig("{}/{}.jpg".format(target_folder,count))
count=count+1
# if count>100:
# break
Result
Flickr8k Dataset
Some images generated from the model



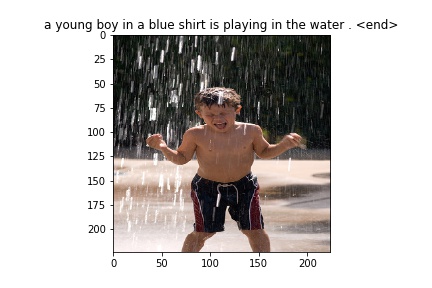
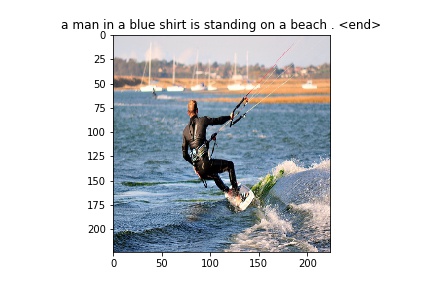
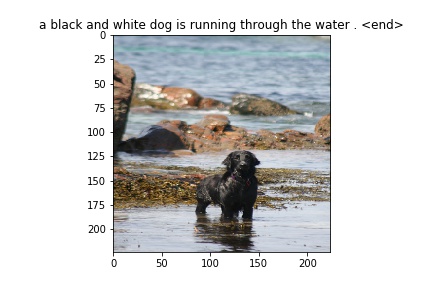
Bengali Images
Hint: Its worse
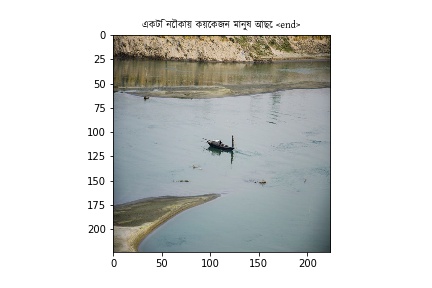


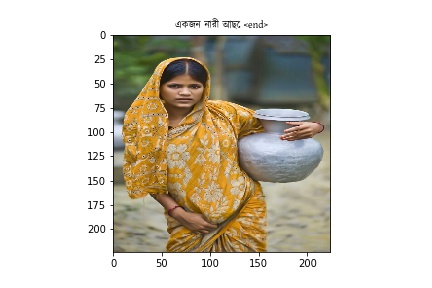
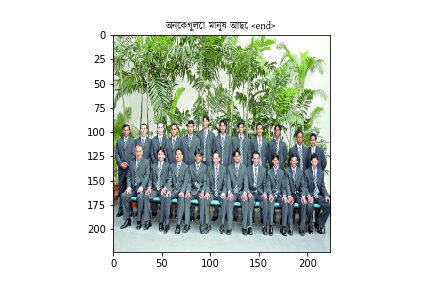

Future of Improvements
Another way to say where did I messed up
Bleue Score
There is a method to evaluate models of caption generation. Bleue score. I didnt calculate them, firstly because, I am already very tired , secondly , i dont know how to do so.
Beam Search
The paper actually implemented beam search. I didnt. I used greedy search ,which is not the best way to generate sequences . It should be implemented
Attention
Part of the reason why I am very tired is because, I tried to implement the 2016 paper of Show attend and tell as well. But the results came much worse. so I didnt publish!
So what?!

